
Google’s security team has discovered serious vulnerabilities in Samsung chips used in numerous Android devices, wearables, and vehicles. These flaws could be exploited if left unpatched, prompting Google to advise disabling VoLTE and Wi-Fi calling.
In a recent blog post, Tim Willis, the head of Google’s Project Zero, reported the team had uncovered 18 zero-day vulnerabilities in Samsung’s Exynos modems, including four top-severity flaws that could potentially compromise devices remotely. Among the affected devices are the Pixel 6 and 7, Samsung phones, and wearables.
In November 2022, Project Zero accused Google and Android manufacturers of failing to address vulnerabilities.
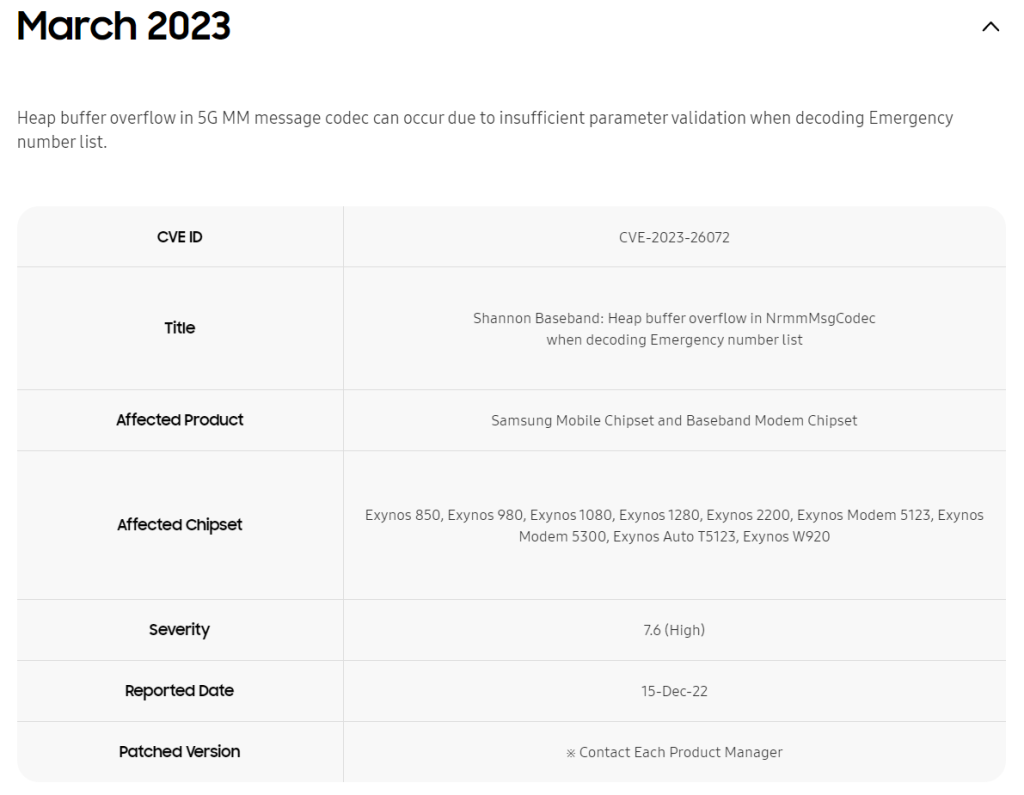
Project Zero exposed 180-day vulnerabilities in Samsung Semiconductor’s Exynos Modems
Project Zero, renowned for discovering 0-days, recently disclosed 18 vulnerabilities in Exynos modems during late 2022 and early 2023. Among these vulnerabilities, four (CVE-2023-24033 included) allow an attacker to execute remote code from the internet to the baseband level of a phone with no user interaction, requiring only the victim’s phone number.
End-users still don’t have patches 90 days after report…. https://t.co/dkA9kuzTso
— Maddie Stone (@maddiestone) March 16, 2023
Project Zero confirms that skilled attackers could develop an operational exploit to compromise affected devices remotely and silently with limited additional research and development. The remaining 14 vulnerabilities are considered less severe, requiring a malicious mobile network operator or an attacker with local access to the device.
Project Zero has made a policy exception to delay the disclosure of the four internet-to-baseband vulnerabilities due to the unprecedented access and the likelihood of an operational exploit being swiftly crafted.
List of Affected Devices
Samsung Semiconductor has released advisories identifying the Exynos chipsets that are vulnerable to security flaws. Based on public information, the following devices are likely affected:
- Mobile devices from Samsung, including the S22, M33, M13, M12, A71, A53, A33, A21, A13, A12, and A04 series
- Mobile devices from Vivo, including the S16, S15, S6, X70, X60, and X30 series
- Pixel 6 and Pixel 7 series from Google
- Wearables that use the Exynos W920 chipset
- Vehicles that use the Exynos Auto T5123 chipset
- The Samsung Galaxy Watch 4 and 5, as well as the Pixel 6 (Exynos 5123) and 7 (Exynos 5300), are also affected.
- Google has already addressed the main CVE-2023-24033 vulnerability in the March 2023 security patch.
Project Zero advises Turn Off VoLTE and Wi-Fi Calling
Since manufacturers may have varying patch timelines. While waiting for fixes, As a precaution, Project Zero advises turning off Wi-Fi calling and VoLTE to remove exploitation risks.
It is recommended to update devices regularly to address disclosed and undisclosed security vulnerabilities. For Pixel 6, 6 Pro, and 6a users, the March 2023 security update has not been released, leaving them vulnerable.
Announcing the findings, Tim Willis, Project Zero, said,
Tests conducted by Project Zero confirm that those four vulnerabilities allow an attacker to remotely compromise a phone at the baseband level with no user interaction, and require only that the attacker know the victim’s phone number. With limited additional research and development, we believe that skilled attackers would be able to quickly create an operational exploit to compromise affected devices silently and remotely.
