Google has unveiled its plans to introduce advanced cellular security features, positioning Android as the pioneering mobile operating system to implement these measures. The enhanced security features will be accessible to both consumers and businesses.
Key Features Introduced in Android 14
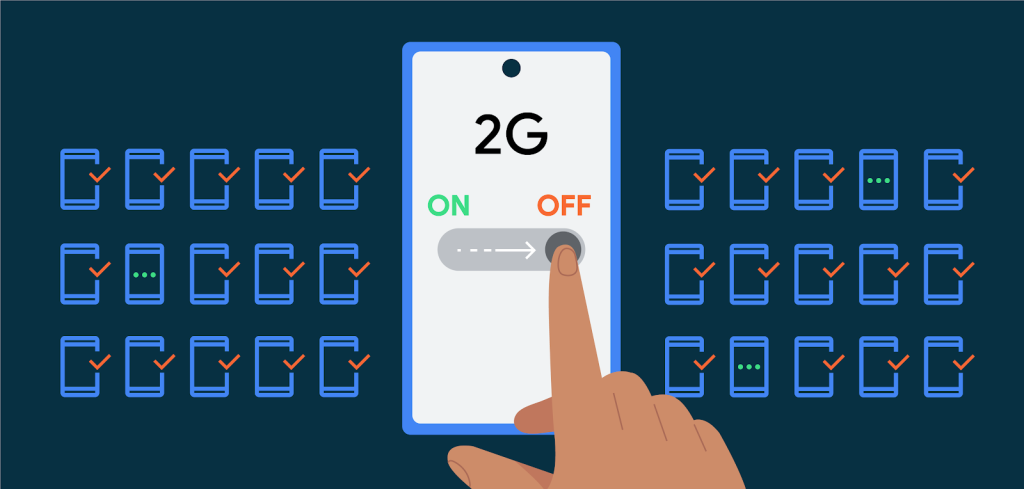
- Disabling 2G Support: Android 14 introduces a vital feature that empowers IT administrators to deactivate 2G support on managed devices. This measure is of significant importance due to inherent vulnerabilities associated with 2G networks. By disabling 2G support, the risk of potential attacks and downgrades to less secure networks is mitigated.
- Null-Ciphered Cellular Connectivity Disabling: Android 14 also addresses the security gap posed by null-ciphered cellular connections. While IP-based user traffic is end-to-end encrypted, circuit-switched voice and SMS data remain exposed. Android 14 introduces a user option to disable null-ciphered connections at the modem level, enhancing communication privacy and safeguarding sensitive information.
Enhancing Android Network Security
The Android Security Model assumes a hostile network environment to safeguard users from network threats. The approach relies on end-to-end encryption (E2EE) for all network traffic to counteract packet injection, tampering, and eavesdropping.
Challenges in Cellular Telephony Security
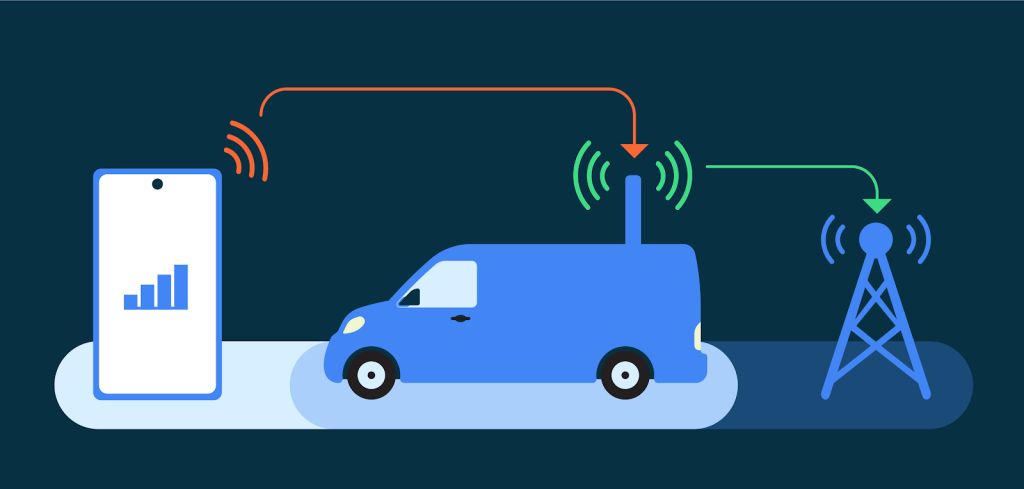
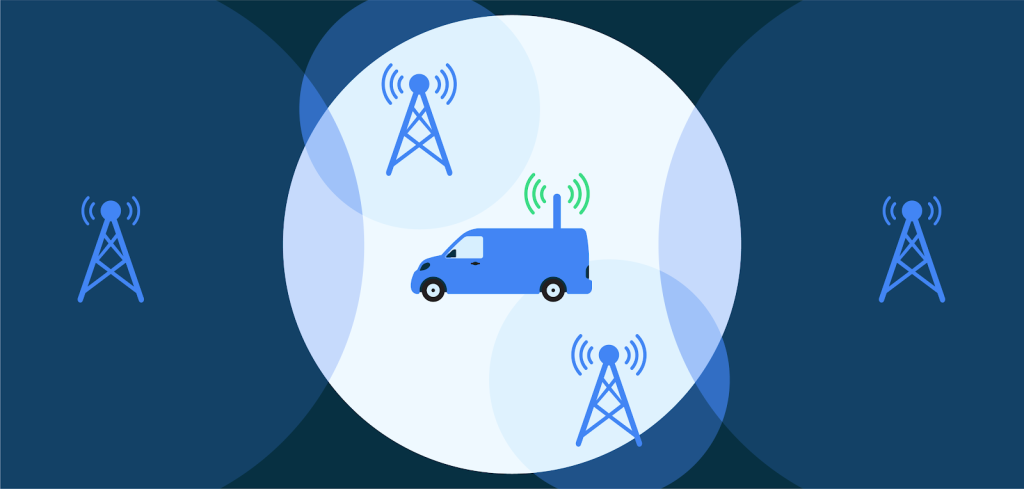
Cellular networks present unique security challenges due to potential exploitation by False Base Stations (FBS) and Stingrays. Android acknowledges these risks and is actively engaged in enhancing cellular telephony security.
Addressing 2G’s Inherent Security Risks
2G networks, established in 1991, lack advanced security measures seen in subsequent generations. The absence of mutual authentication in the Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) standard renders 2G vulnerable to Person-in-the-Middle attacks.
The 2G network’s outdated security combined with the potential for forced downgrades significantly exposes users to threats like FBSs, IMSI catchers, and Stingrays.
Enterprise-Level Protection
Enterprises relying on smartphones and tablets demand robust security for sensitive data.
- Android Enterprise offers comprehensive management controls for connectivity security, including disabling Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and data signaling over USB.
- Android 14 enhances enterprise security by allowing IT administrators to prevent devices from downgrading to 2G connectivity.
Tackling Null Ciphers
Android 14 addresses security risks associated with null-ciphered connections in cellular networks. While IP-based traffic is E2EE, voice and SMS data are exposed due to the cellular link layer cipher.
Android 14 empowers users to disable support for null-ciphered connections, ensuring privacy for devices with the latest radio hardware abstraction layer.
Collaboration for Cellular Security
Google actively engages in developing cellular security standards through partnerships with industry bodies like GSMA Fraud and Security Group and 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP). Efforts are underway to modernize identity, trust, and access control techniques to bolster telco network security.
In upcoming Android releases, Google envisions introducing further security features to tackle cellular threats. They invite collaboration with partners and standardization bodies to collectively advance telco network security and overcome FBS threats.
